Wikipedia defines Docker as
an open-source project that automates the deployment of software applications inside containers by providing an additional layer of abstraction and automation of OS-level virtualization on Linux.
What is a Dockerfile
Dockerfile is a script, composed of various commands (instructions) and arguments listed successively to automatically perform actions on a base image in order to create (or form) a new one. They are used for organizing things and greatly help with deployments by simplifying the process start-to-finish. The following are the steps to create your first docker image.
- Create a Dockerfile
- Build the dockerfile to create image
- Run the image to create container.
Dockerfile Commands
There are a dozen commands but we will touch a few of them that are useful in building a docker image.
FROM
This is the most important among all the commands. This defines the base image which is used to build the process. If FROM is not found locally on the host, Docker will try to download from the Docker hub.
# Usage: FROM [image name]
FROM ubuntu
MAINTAINER
This declares the author/creator of the dockerfile. This just helps for future references.
# Usage: MAINTAINER [name]
MAINTAINER authors_name
RUN
The RUN command is the central executing directive for Dockerfiles. It takes a command as its argument and runs it to form the image. Unlike CMD, it actually is used to build the image (forming another layer on top of the previous one which is committed).
# Usage: RUN [command]
RUN aptitude install -y riak
CMD
The CMD is similar to RUN and can be used to execute commands. CMD is executed after the container has started.
# Usage 1: CMD application "argument", "argument", ..
CMD "echo" "Hello World!"
VOLUME
The VOLUME command is used for persisting data generated by Docker containers. Using this command the storage is shared among containers and also between host and the containers
# Usage: VOLUME ["/dir_1", "/dir_2" ..]
VOLUME ["/my_files"]
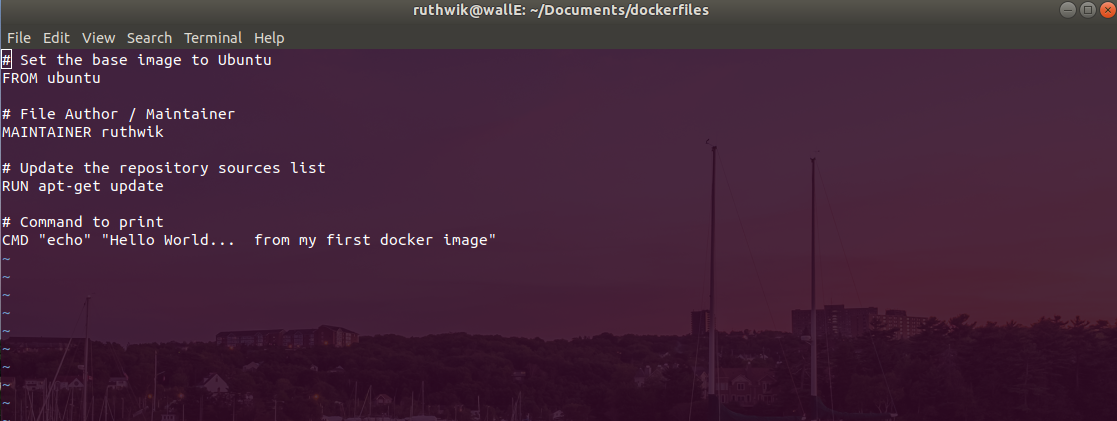
1. Create a Dockerfile
Using a texteditor create a Dockerfile (remember without any extension)
Set the base image
A base image is used to create the container image. A base image can be an offical Docker image. Here in our Dockerfile we will be using ubuntu as our base image
# Set the base image to Ubuntu
FROM ubuntu
MAINTAINER/AUTHOR
# File Author / Maintainer
MAINTAINER ruthwik
Setting up the commands
# Update the repository sources list
RUN apt-get update
# Command to print
CMD "echo" "Hello World... from my first docker image"
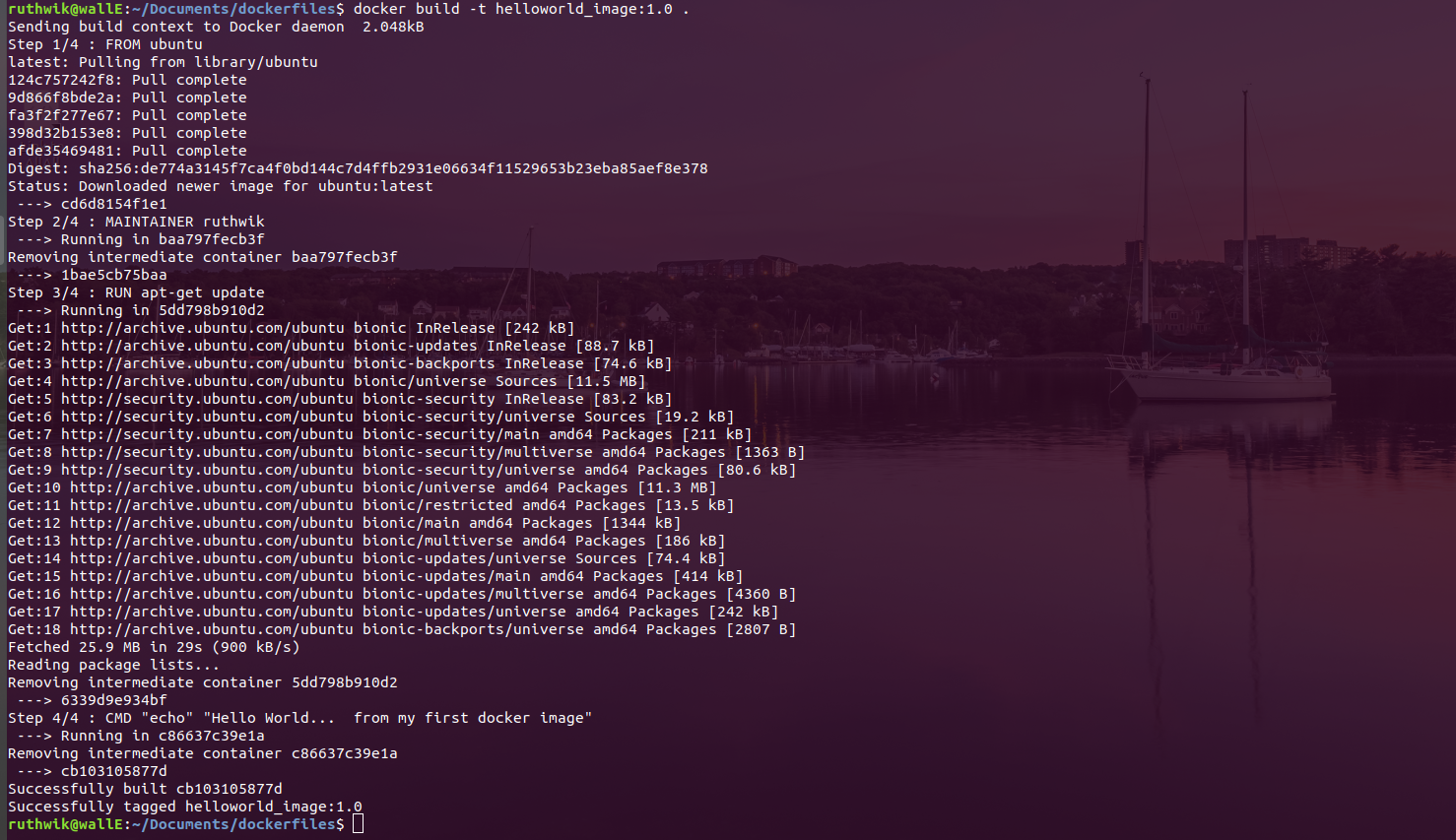
2. Build the dockerfile to create image
Use the following to create your first image
docker build -t ImageName:Tag directoryOfDocekrfile
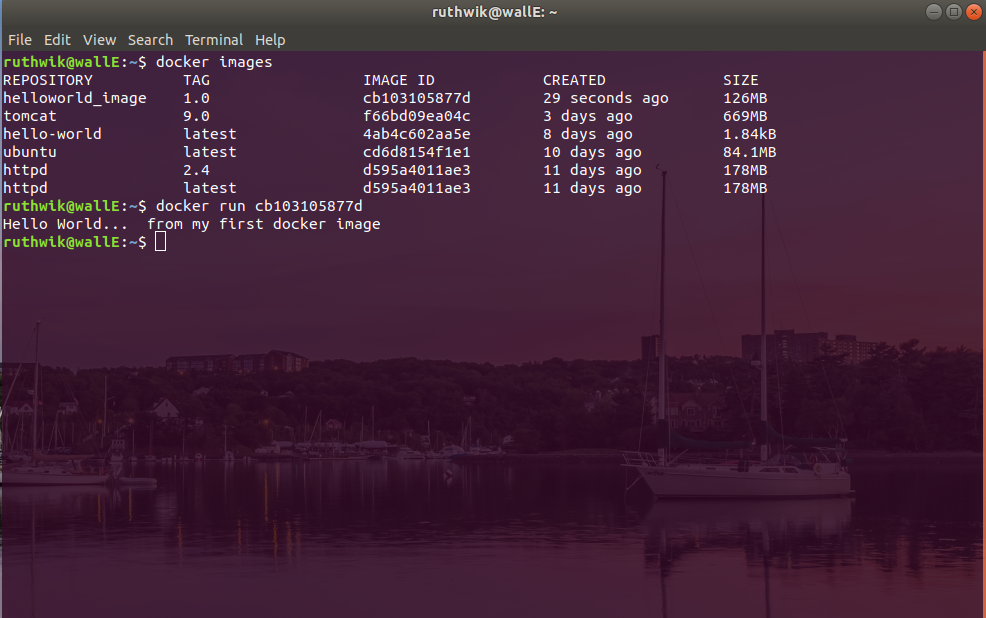
3. Run the image to create container
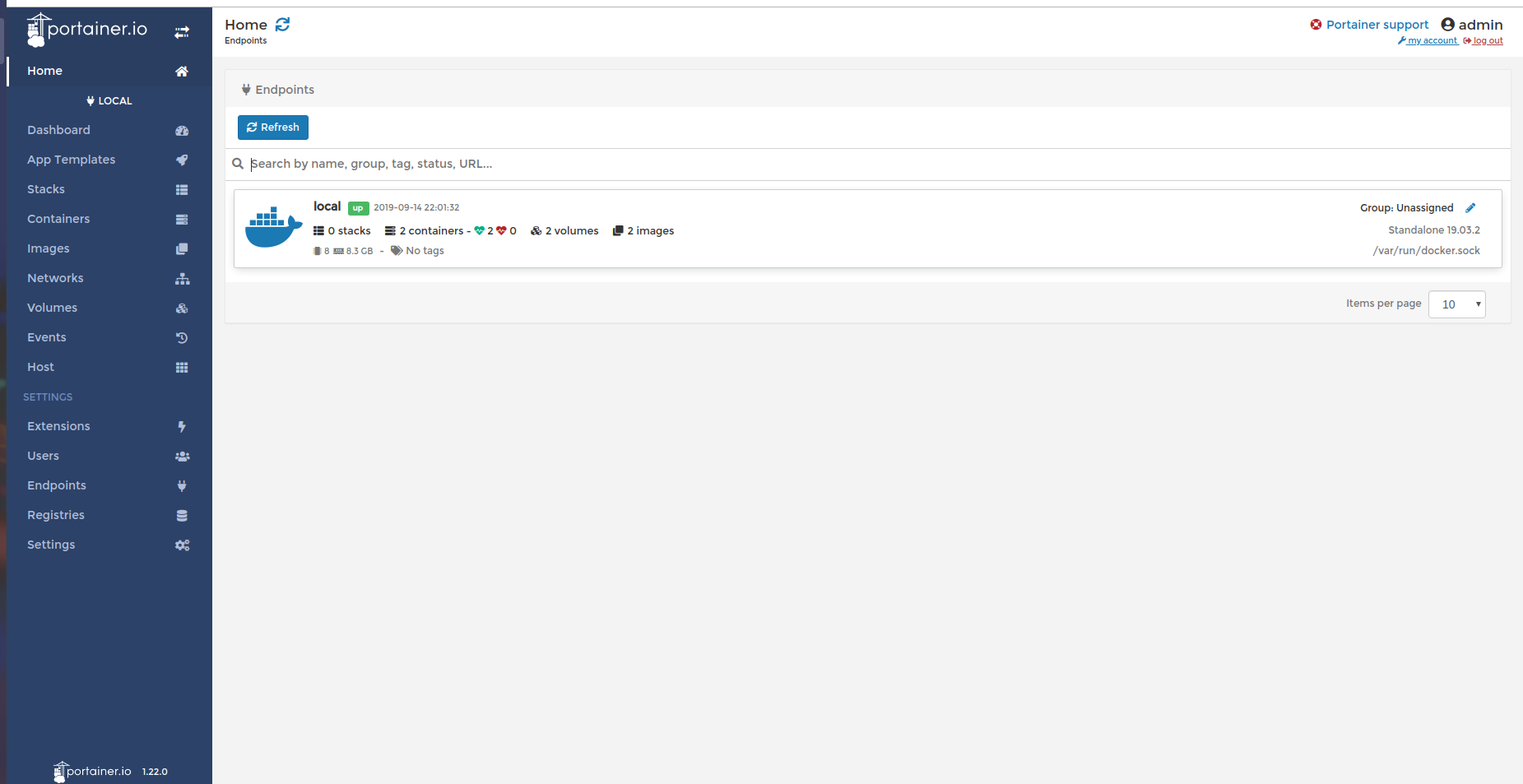
Portainer
Portainer is a lightweight management UI which allows you to easily manage your different Docker environments (Docker hosts or Swarm clusters).
Pull and Run the image
docker pull portainer/portainer
docker volume create portainer_data
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 -p 9000:9000 -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer
Login to Adminpage

Portainer Home page
Portainer Dashboard

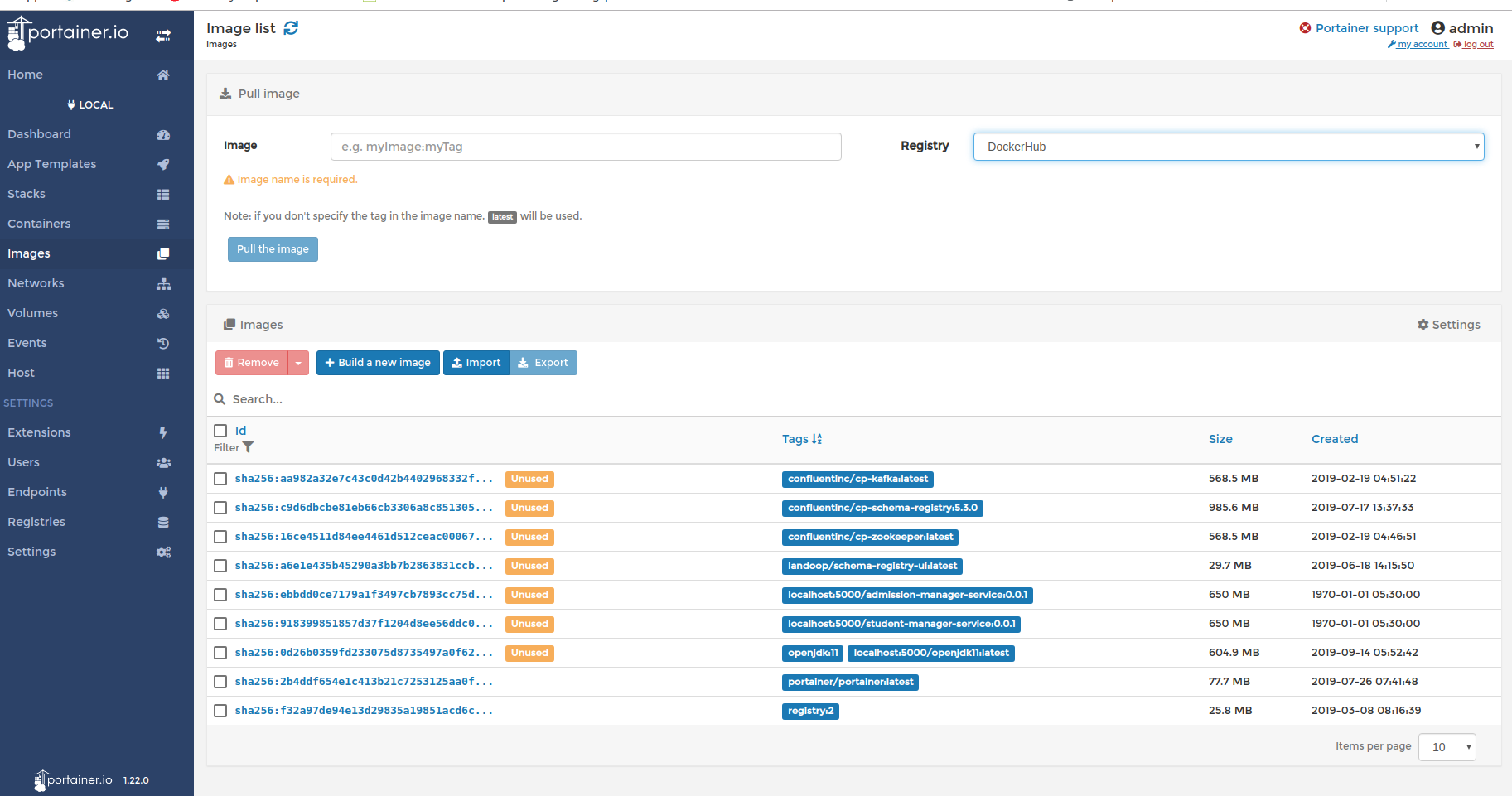
Check the list of images
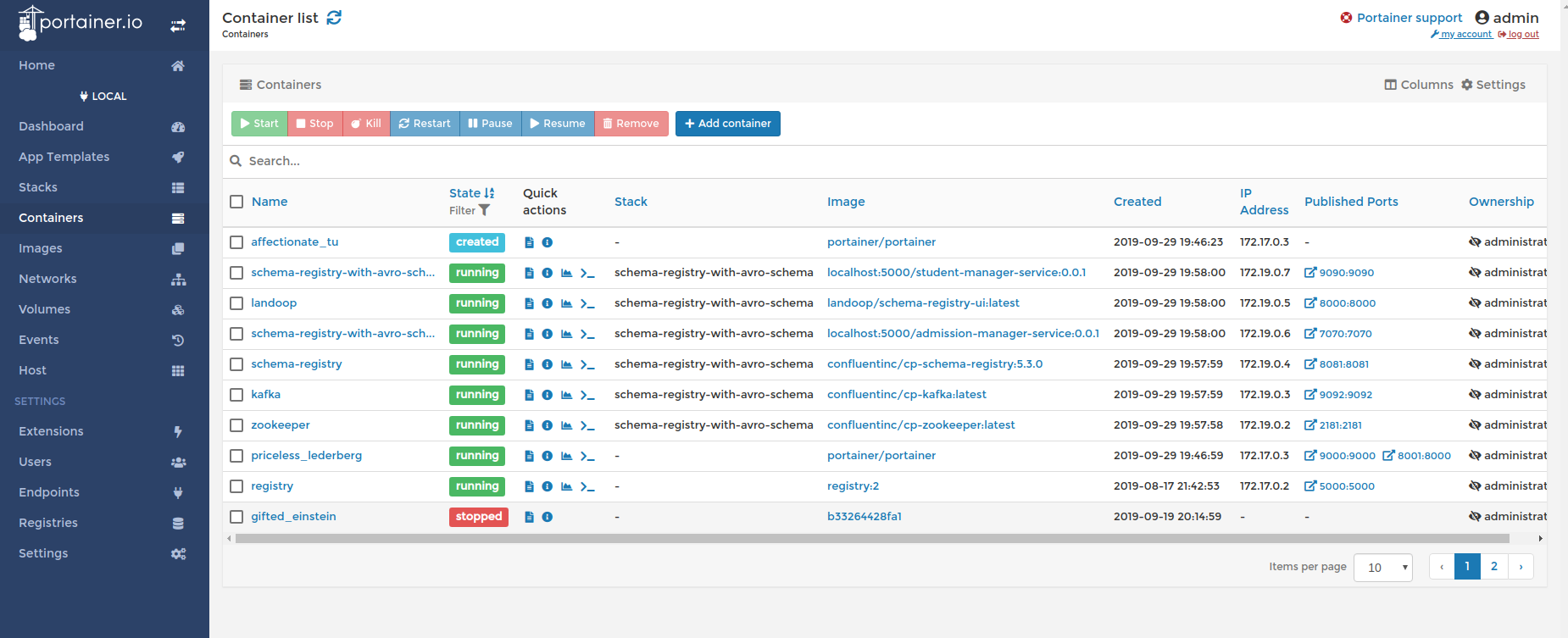
Check the list of containers
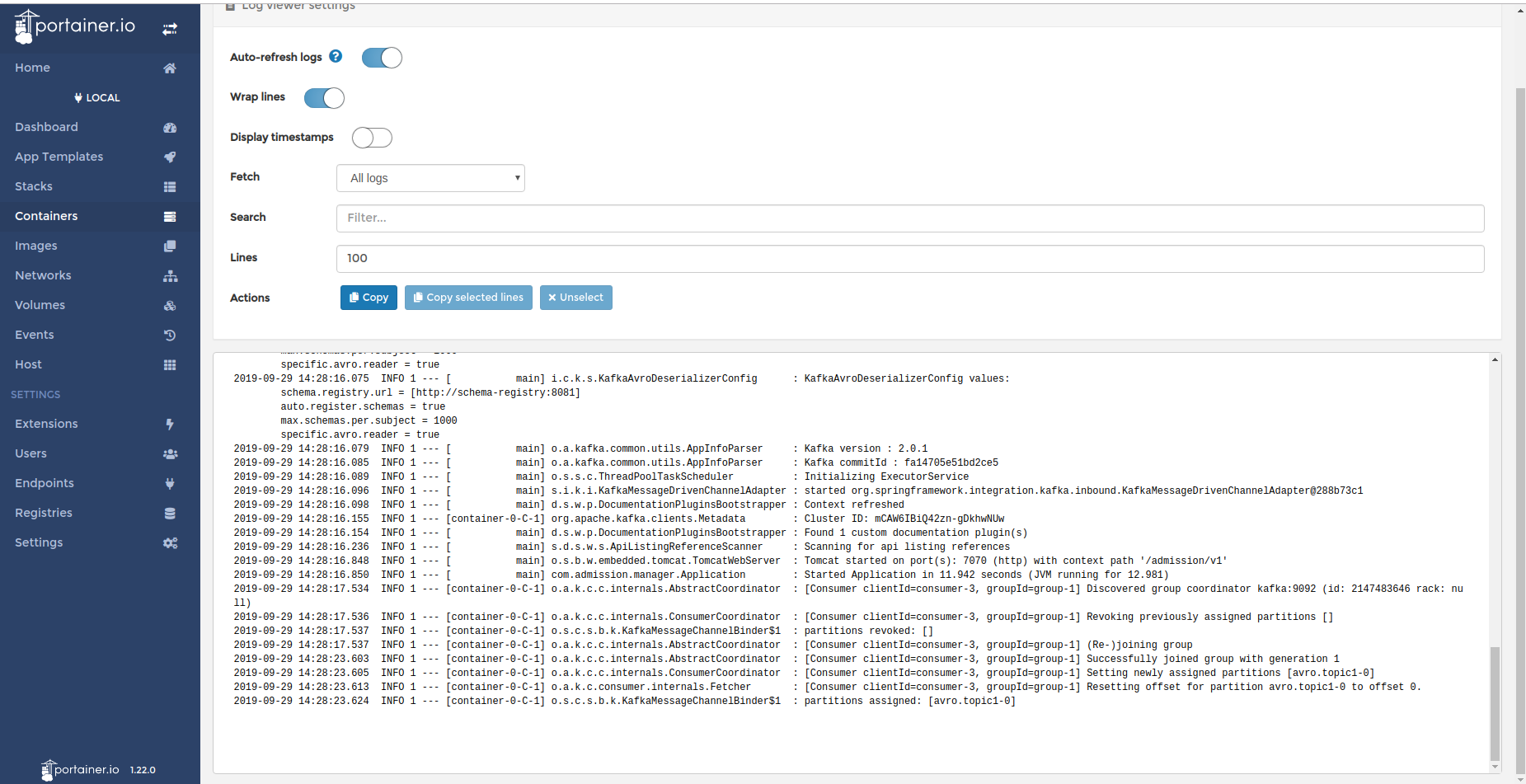
Container logs
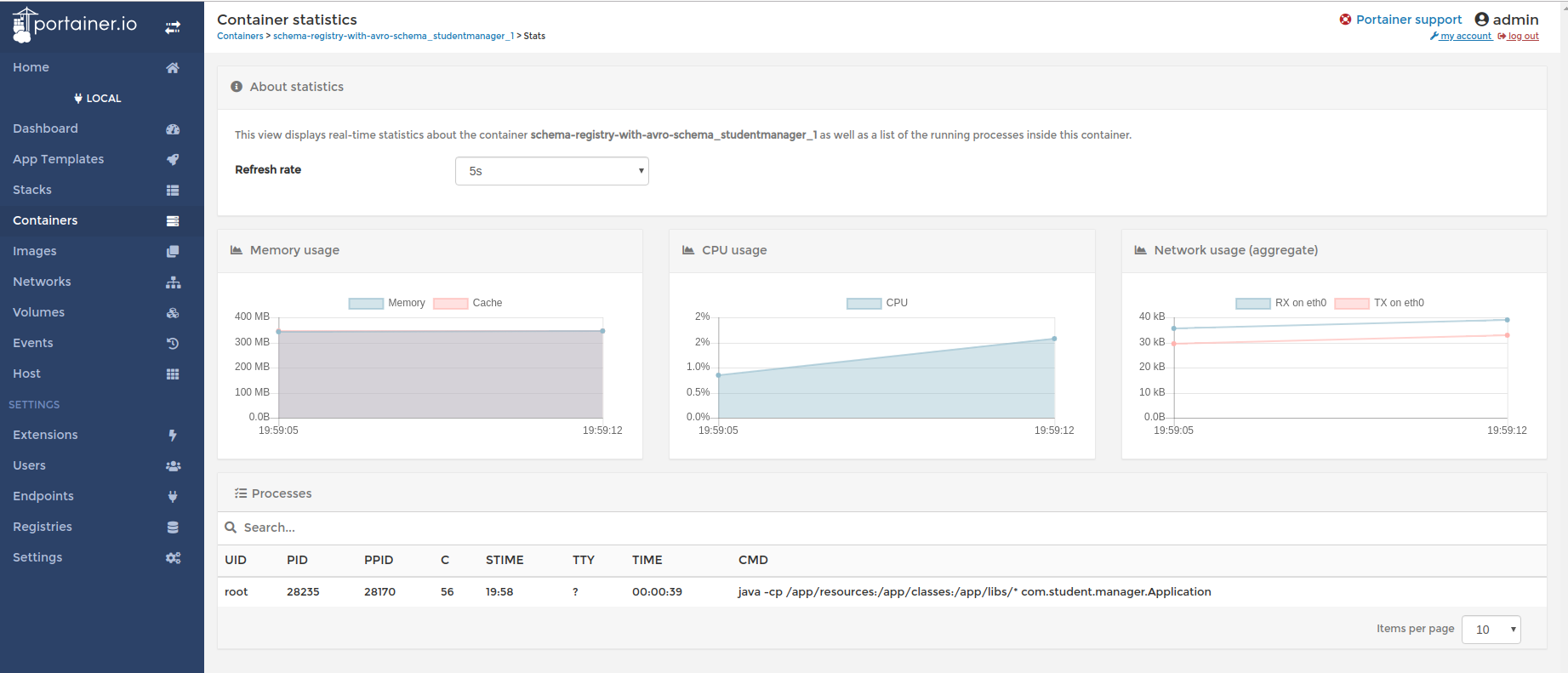
Container statistics
If you have any question or feedback, please do reach out to me by commenting below.